INTRODUCTION TO PLANT MORPHOLOGY
Information about an institutional herbaria is available at this link to the University of British Columbia Beaty Biodiversity Museum [New Tab].[2]
Digital databases and apps typically use the morphology of stems, leaves, flowers, and fruit to identify unknown plants . Examples of regional databases are available at these links to the Kwantlen Polytechnic University Plant Database [New Tab][3], Oregon State University Landscape Plants [New Tab][4], and University of British Columbia E-Flora BC [New Tab][5].
STEM MORPHOLOGY
A morphological description usually starts with the structure of a plant. Plant stems with vascular tissue support leaves and reproductive structures such as flowers. Depending on the type of plant, stems may be woody or herbaceous, and solid or hollow in cross section.
Herbaceous (non-woody) stems with solid or hollow stems are typical of forbs (eudicots), grasses, and grass-like plants called rushes and sedges (monocots). The stems are generally filled with a soft spongy tissue called pith, that stores and transports nutrients. The culm (stem) of a grass plant (Poa spp.) is hollow with pith only at the jointed nodes. The base of the leaf circles around the stem forming a series of overlapping sheaths. Sedges (Carex spp.), differ from grasses and rushes in that the stems are triangular (V-shaped) in cross section at the base (“sedges have edges”), have a solid pith, and are not jointed. Rushes differ from grasses in that stems are not jointed (no nodes) and are typically filled with pith. Some rush genera, such as Luzula spp. can look very grass-like with leaf blades while in Juncus spp. the leaves may be reduced to just a rounded sheath. Examples of these morphological characteristics are available at this link to Grasses, Sedges and Rushes [New Tab][6].
In contrast to herbaceous stems that die at the end of the growing season, woody stems are permanent structures that grow in length and girth (diameter) each year and produce bark as a protective covering. The general features of the woody stem illustrated in Figure 13.1 will be characteristic for a particular plant species.
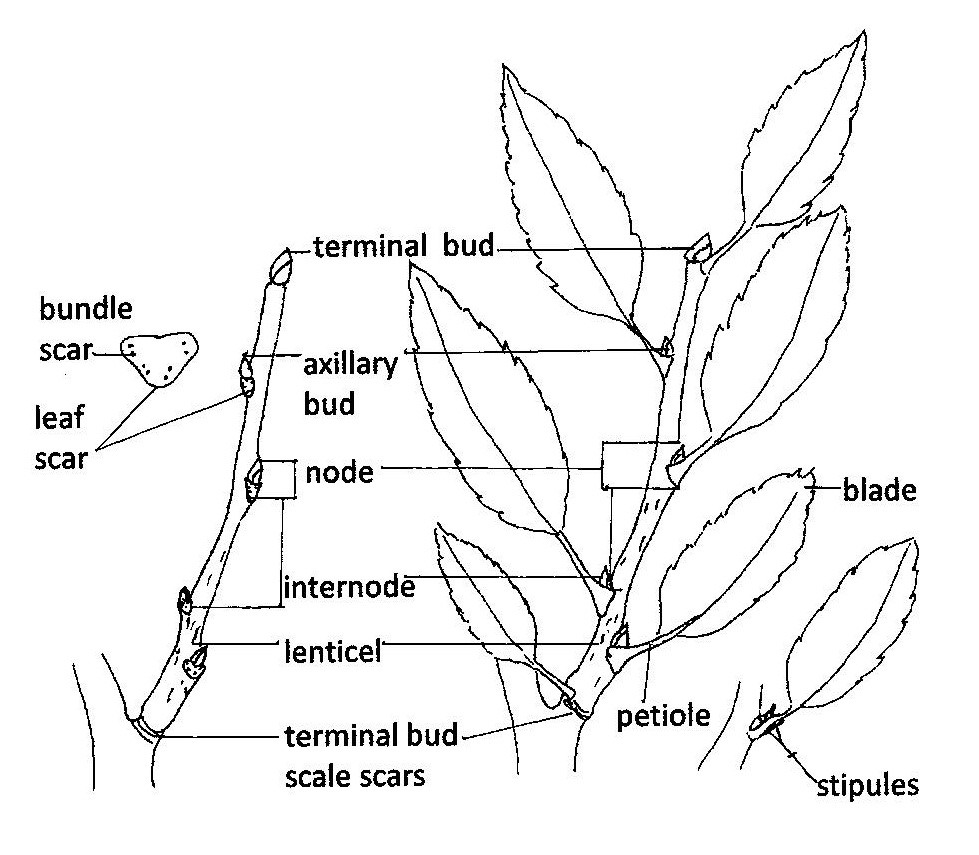
The shape, size and arrangement of buds and lenticels (small openings in the outer bark that allow for the exchange of gases), are often identifiable in trees and shrubs, as shown in Figure 13.2 and Figure 13.3. The thickness, texture, pattern, and color of the bark of many woody plants is both a distinctive species characteristic for identification and an attractive feature for landscape use.


Examples of the morphology of herbaceous stems and woody stems and buds are available at this link to Stems – External KPU.ca/Hort [PDF] [New Tab][7].
Stem modifications include underground, above ground, and aerial structures that are characteristic to different plant species. Underground structures for spreading and food storage include rhizomes, corms, tubers, and bulbs. Stolons, runners, suckers, and offsets that grow almost parallel to or just above the ground enable plant spread. Aerial modifications include stem tendrils and thorns for climbing and protection. In xeric (dry) conditions, the stem may take over photosynthesis in order to reduce water loss from leaves (Cactus spp.). Examples of different types of stem modifications are shown at this link to Modifications – Stem KPU.ca/Hort [PDF] [New Tab][8].
Comments
Post a Comment